Lecture on the topic: "The role of information activity in modern society: economic, social, cultural, educational spheres." Lecture: The role of information activity in modern society The role of information activity in modern society
Introduction…………………………………………………………………………………...3
The role and importance of information in society……………….……………..…...4
Man in the information space……………………………9
Conclusion………………………………………………………..………11
Used literature………………………………….………….....12
INTRODUCTION
In the beginning there was the word. And also gesture, drawing, dance, smoke from fires and other simple ways of transmitting information that people learned to use at about the same time as primitive tools.
Then the word became written. This was very convenient - it became possible to entrust legends, folk tales, epics, as well as personal and state correspondence to hard media. Couriers no longer needed to memorize messages; bureaucracy and paperwork appeared.
The greatest inventions of mankind were the printing press and regular mail.
They gave rise to two main signs of civilization - a person should be able to regularly correspond with any number of respondents and read the latest news in newspapers.
Informatization will ensure the transition of society from an industrial type of development to an information one. The information market will provide consumers with all the necessary information products and services, and their production will be provided by the computer science industry, often called the information industry.
ROLE AND IMPORTANCE OF INFORMATION IN SOCIETY
In the history of the development of civilization, several information revolutions have occurred - transformations of social relations due to fundamental changes in the field of information processing. The consequence of such transformations was the acquisition of a new quality by human society.
The first revolution was associated with the invention of writing, which led to a gigantic qualitative and quantitative leap. There is an opportunity to transfer knowledge from generation to generation.
The second (mid-16th century) was caused by the invention of printing, which radically changed industrial society, culture, and organization of activities.
The third (late 19th century) was due to the invention of electricity, thanks to which the telegraph, telephone, and radio appeared, making it possible to quickly transmit and accumulate information in any volume.
The fourth (70s of the XX century) is associated with the invention of microprocessor technology and the advent of the personal computer. Computers are created using microprocessors and integrated circuits, computer networks, data transmission systems (information communications). This period is characterized by three fundamental innovations:
1) transition from mechanical and electrical means of conversion
information to electronic;
2) miniaturization of all components, devices, instruments, machines;
3) creation of software-controlled devices and processes.
The latest information revolution brings to the fore a new industry - the information industry, associated with the production of technical means, methods, technologies for the production of new knowledge. All types of information technologies, especially telecommunications, are becoming the most important components of the information industry.
The increasing complexity of industrial production, social, economic and political life, changes in the dynamics of processes in all spheres of human activity have led, on the one hand, to an increase in the need for knowledge, and on the other, to the creation of new means and ways to satisfy these needs.
The rapid development of computer technology and information technology gave impetus to the development of a society built on the use of various information and called the information society.
The information society is a sociological and futurological concept that considers the production and use of scientific, technical and other information to be the main factor in social development. In the 50-70s, it became obvious that humanity was entering a new era, the road to which was paved by the rapid development of technology and, first of all, computers, and scientific and technological revolution in general. It is interesting to note that almost all proposed names have the Latin prefix “post-”, i.e. “after -”, as if their creators were expecting some kind of worldwide cataclysm, a global revolution in technology and in the consciousness of people, after which a new era would suddenly begin, new era
, a new society will emerge. That is why it was so important to find a fundamentally new name, simultaneously showing the continuity and fundamental novelty of the coming society. And this name became the “information society” invented by Toffler.
Thus, the “information society” is a civilization, the development and existence of which is based on a special intangible substance, conventionally called “information”, which has the property of interaction with both the spiritual and material world of man.
Modern society cannot exist in conditions of sensory hunger - a comprehensive information field is absolutely necessary for its development and self-organization.
In the process of developing an information strategy, it is important to consider that when creating information environment a dialectical unity of computer science and social information systems must be formed.
Unfortunately, in scientific literature and journalism the information environment is often interpreted as synonymous with the technosphere, which is a reflection of the technocratic approach. Nowadays, throughout the world, in the process of informatization, the development of software and hardware means of informatization (“hardware” + software) strongly prevails. A paradoxical situation develops when very high-quality technology processes low-quality information that is inadequate to social processes.
The most important concept that needs to be defined when studying the information environment of society is the concept of “information potential of society”. The information potential of society in a broad sense is the information resource accumulated in society. The information potential of society in the narrow sense is an activated, put into action information resource. The information potential of society is the information resource of society in unity with the means, methods and conditions that allow it to be activated and used effectively.
Thus, the unity of the processes of computerization, mediatization and intellectualization is necessary.
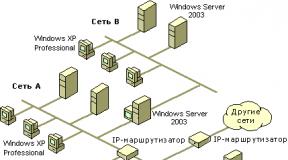
In the future information society, global information communications will be of decisive importance. The basis for such communications can be the international computer network Internet. The birthplace of the Internet is the United States of America. The Internet has become a development of military technology. The progenitor was the ARPAnet network (Advanced Research Project Agency net - the network of the Advanced Research Projects Agency), developed and deployed back in 1969 by order of the US Department of Defense. While experimental, ARPAnet was created to support scientific research in the military-industrial sphere. In particular, methods were studied for constructing networks that would be resistant to partial damage, for example, during aircraft bombing, and would retain the ability to function normally in such extreme conditions.
The APRAnet model provided for a constant connection between the source computer and the destination computer (destination station) - a network, according to the condition, which was assumed to be unreliable; any part of it could disappear at any moment. Not only the network as a whole, but also the communicating computers were responsible for establishing and maintaining communication. The basic principle was that any computer could communicate peer-to-peer with any other computer connected to the network.
As ARPAnet grew, other networks also developed, for communication between which so-called gateways were used, which allowed information to freely flow from one network to another.
The standard according to which the Internet could develop was established in 1983. And from this moment it became possible to add gateways and
connect new networks to it, while the original core remained unchanged. Most analysts believe that it was 1983. - the actual date of the Internet's origins, when the original ARPAnet was divided into the MILNET network intended for military use, and the ARPAnet itself, aimed at continuing research in the network field. ARPAnet itself ceased to exist in June 1990. and I will gradually transfer its functions to a more extensive structure of the Internet. Perhaps it was then that it was possible for the first time to demonstrate the reliability of the Internet as a means of communication, since the closure and, accordingly, the shutdown of ARPAnet - the ancestor of the Internet - did not in any way affect the operation of the network as a whole. In 1985 the number of networks connected to the Internet approached one hundred by 1987. their number doubled, and in 1989 it reached five hundred. Today, the Internet consists of more than 12 thousand interconnected networks.
The path paved by the Internet will determine many elements of the future highway. The Internet is a wonderful, vital development, one component of the final system, but it will change significantly in the coming years. The modern Internet lacks security and a billing system. Technologies that will embody the idea of a universal information highway have yet to develop to the required level. This will be a single high-bandwidth network - a connection of computer and other communications.
PERSON IN THE INFORMATION SOCIETY Representations of the authors of the concept “” about human life in a new society are slightly fabulous and utopian.
Such are the idyllic dreams and castles in the air of J. Martin and some other authors not cited here. They are guided by the idea that they can make a person happy by solving all his material problems, getting rid of work and providing long leisure. As has been proven time and time again, this is a completely wrong point of view.
On the one hand, information forms the material environment of human life, acting as innovative technologies, computer programs, telecommunication protocols, etc., and on the other hand, it serves as the main means of interpersonal relationships, constantly emerging, changing and transforming in the process of transition from one person to another. to another. Thus, information simultaneously determines both the sociocultural life of a person and his material existence.
The problem of human existence and existence in a completely “technical” and “informatized” world could not help but occupy philosophers, which gave rise to the concept of an “information” society. None of the philosophers who wrote about this problem doubted the radical renewal of all human life within the framework of this new formation, but most of them analyzed the problem one-sidedly, whether from a political, economic or social point of view.
Unfortunately, the authors of the concept of the “information society” did not devote enough space to consider the question of what consequences its onset will bring for the cultural life of mankind. This question was specifically developed only by Toffler in his books “The Third Wave” and articles on the future of work. In connection with the coming onset of the “information age,” the main task is to speed up and simplify the transfer of information between people as much as possible and increase its “digestibility.” That is why it is standardized and classified in order to speed up the process of processing information flow as much as possible. This process affects culture in two ways: on the one hand, the spiritual and material aspects of human life come as close as possible, because in culture there is necessarily an information element undergoing the transformations described above, and on the other hand, there is a sharp distinction between the emotional and informational aspects of culture.
CONCLUSION
Modern science and technical creativity are drawing fundamentally new types of objects into the orbit of human activity, the development of which requires new strategies. We are talking about objects that are self-developing systems characterized by synergistic effects. Their development is always accompanied by the passage of the system through special states of instability (bifurcation points), and at these moments small random influences can lead to the appearance new structures, new levels of system organization that influence existing levels and transform them.
Information is, firstly, knowledge of a relatively new type, suitable for further use, and secondly, knowledge, the production, storage and application of which is indeed becoming an increasingly important activity for society, giving rise to corresponding technical and organizational structures. The increasing role of information and information systems is a historical fact that underlies the concepts of the information society. Another fact is the rapid, truly revolutionary impact of “information intelligence” on production, management, and the entire life of people.”
Today, according to experts, 90% of all transport movements of people are associated with information purposes (meetings, signatures, certificates, etc.). Modern “homework” sharply reduces the required time for people to be present at workplaces and in educational institutions. This will require a radical restructuring of production and educational processes, a significant increase in the culture and consciousness of people, as well as the development of a new control and evaluation apparatus.
Have political parties, ... society. IN various systems situation, media information different: if in democratic societies mass media information...using amplification roles punitive authorities...
Role and place of education in society
Abstract >> SociologyDepartment of Sociology Role and place of education in society Completed by: Chernitsina... childhood. Generally meaning preschool education is underestimated. ... Role Education in economics is broader than production aspects. It manifests itself in the consumption of goods, information ...
Information activities- activities that ensure the collection, processing, storage, search and dissemination of information, as well as the formation of an information resource and the organization of access to it.
Information has always played an extremely important role in human life. Whoever has the most information on any issue is always in a better position than others. It is a well-known saying that whoever owns the information owns the world.
Since ancient times, collecting and systematizing information about the world around us has helped people survive in difficult conditions - experience and skills in making hunting and labor tools, creating clothing and medicines have been passed on from generation to generation. The information was constantly updated and supplemented - each studied phenomenon made it possible to move on to something new, more complex.
Over time, large volumes of data about the surrounding world contributed to the development of scientific and technological progress and, as a result, of society as a whole - people were able to learn to manage various types of matter and energy.
Over time, the role of information in human life has become more and more significant. Now, in the first half of the 21st century, the role of information in a person’s life is decisive - the more skills and knowledge he has, the higher he is valued as a specialist and employee, the more respect he has in society.
In recent decades, there has been persistent talk about the transition from an “industrial society” to an “information society.”
Information has become one of the most important strategic and management resources, along with resources - human, financial, and material. The use of microprocessor technology, electronic computers and personal computers led to a radical transformation of relations and technological foundations of activity in various spheres of public life: production and consumption, financial activity and trade, the social structure of society and political life, the service sector and spiritual culture.
If we consider information activities in economic sphere, then the main goal information technologies- as a result of targeted actions to process primary data, obtain the information necessary for the user. For example, there is data about some kind of production: the cost of raw materials, energy costs, workers' wages, etc. It is necessary to calculate the cost of the goods received, profit. You can count manually using known formulas, or you can already use ready-made programs, which will calculate everything and provide the information necessary for the user.
That is, an economic information system is a system whose functioning over time consists of collecting, storing, processing and disseminating information about the activities of any real economic entity.
IN modern world The role of computer science, means of processing, transmitting, and storing information has increased immeasurably. Information science and computer technology now largely determine the scientific and technical potential of the country, the level of development of its national economy, the way of life and human activity. Rothschild also said: “He who owns information owns the world.”
For the purposeful use of information, it must be collected, transformed, transmitted, accumulated and systematized. All these processes associated with certain operations on information are calledinformation processes . Receiving and converting information is a necessary condition for the life of any organism.
Living beings are capable of not only perceiving information from the environment using their senses, but also exchanging it with each other. A person also perceives information through the senses, and languages are used to exchange information between people. During the development of human society, many such languages arose. First of all, these are native languages (Russian, Tatar, English, etc., spoken by numerous peoples of the world. The role of language for humanity is extremely great. Without it, without the exchange of information between people, the emergence and development of society would be impossible.
Information processes are characteristic not only of wildlife, humans, and society. Humanity has created technical devices - automata, the work of which is also associated with the processes of receiving, transmitting and storing information. Human activity associated with the processes of receiving, transforming, accumulating and transmitting information is calledinformation activities .
For thousands of years, the objects of human labor have been material objects. All tools from the stone ax to the first steam engine, electric motor or lathe were associated with the processing of matter, the use and transformation of energy. At the same time, humanity had to solve management problems, problems of accumulation, processing and transmission of information, experience, and knowledge. Gradually, groups of people emerged whose profession is related exclusively to information activities. However, the number of people who could use information from written sources was negligible. Firstly, literacy was the privilege of an extremely limited circle of people and, secondly, ancient manuscripts were created in single (sometimes only) copies.
A new era in the development of information exchange was the inventionprinting. Thanks to the printing press, knowledge and information became widely replicated and accessible to many people. This served as a powerful incentive for increasing the literacy of the population, developing education, science, and production.
As a result of scientific and technological progress, humanity has created ever new means and methods of collecting, storing, and transmitting information. But the most important thing in information processes - processing, purposeful transformation of information - was carried out until recently exclusively by humans.
The development of science and education has led to a rapid increase in the volume of information and human knowledge. If at the beginning of the last century the total amount of human knowledge doubled approximately every fifty years, then in subsequent years - every five years.
The way out of this situation was the creationcomputers, which greatly accelerated and automated the information processing process.
Currently, computers are used to process not only numerical, but also other types of information. Thanks to this, computer science and computer science have become firmly established in the life of modern people and are widely used in production, design work, business and many other industries.
The development of methods and techniques for presenting information, technology for solving problems using computers, has become an important aspect of the activities of people in many professions.
The role of information activities in modern society The presentation was prepared by the teacher of the Baimak Agricultural College, Musina Zh.M.
The information society is a society in which the majority of workers are engaged in the production, storage, processing and sale of information, especially its highest form - knowledge. 2
Problems of information in general and management as information process paid a lot of attention due to the following objective processes: humanity is experiencing an information explosion. The growth of information circulating and stored in society has come into conflict with a person’s individual abilities to assimilate it; development of mass communication processes; the need to develop a general theory of information; development of cybernetics as a management science; 3
The problems of information in general and management as an information process are given a lot of attention, due to the following objective processes (continued): the penetration of information technologies into the spheres of social life; research in the field of natural sciences confirms the role of information in the processes of self-organization of living and inanimate nature; actualization of the problem of sustainable development, the formation of an information economy, the main driving force of which is information potential and information resources; the problem of the prospects for the development of humanity as an integrity makes it necessary to raise the question of the criterion of progress in modern conditions. 4
Distinctive features: increasing the role of information, knowledge and information technology in the life of society; an increase in the number of people employed in information technology, communications and the production of information products and services in the gross domestic product; the growing informatization of society using telephony, radio, television, the Internet, as well as traditional and electronic media; creation of a global information space ensuring: effective information interaction between people, their access to global information resources, satisfaction of their needs for information products and services. 5
The main characteristics of the information society are determined by the following criteria: Technological: the key factor is information technology, which is widely used in production, institutions, the education system and in everyday life. Social: information acts as an important stimulator of changes in the quality of life, “information consciousness” is formed and established with wide access to information. Economic: Information is a key factor in the economy as a resource, service, commodity, source of added value and employment. Political: freedom of information leading to a political process characterized by increasing participation and consensus among different classes and social strata of the population. Cultural: recognition of the cultural value of information by promoting the establishment of information values in the interests of the development of the individual and society as a whole. 6
As a result of the unification of various information networks, it became possible to create a global information system Internet, which allows you to conduct information service according to the principle “always and everywhere: 365/366 days, 24 hours a day anywhere in the world.” 8
Now information technologies have turned into an independent and quite profitable type of business, which is aimed at satisfying the various information needs of a wide range of users. 9
The use of modern information technologies provides almost instantaneous connection to any electronic information arrays (such as databases, electronic reference books and encyclopedias, various operational reports, analytical reviews, legislative and regulatory acts, etc.) coming from international, regional and national information systems and using them in the interests of successful business. 10
Literature i nformacionnaja_dejatelnost_cheloveka_13_chas , Klyucheva Elena Evgenievna, computer science teacher, State Educational Institution high school No. 378 Kirovsky district. Pervin Yu.A. and others. Robotland: A Book for School. - M.: Scientific Center software training at the Moscow State Conservatory on Public Education, 2001. Smolyan G.L. and others. Information and psychological security (definition and analysis of the subject area). - M.: Institute of System Analysis RAS, 2007. 11
Thank you for your attention 12
Subject:
Target:introduce students to the role of information in modern society.
Tasks:
· educational – an idea of the role of man in the information activities of modern society;
· developing - developing the skills to highlight the main, essential, generalize existing facts, the formation of logical thinking, attention, interest in the subject; development of mutual assistance, speech, and the ability to listen to each other;
· educational - instilling respect for a friend, the ability to behave with dignity, nurturing a culture of communication, working to improve oral literacy.
Questions:
1. Introduction.
2. The role of information activity in modern society: economic, social, cultural, educational spheres.
Theoretical material .
1. Introduction.
Information has always been an important factor in social development. With its help, humanity has concentrated the centuries-old life experience of previous generations. The saying “He who owns the information owns the world” emphasizes social role information. Further social development will, of course, be primarily associated with informatization. Possession of information opens up new management models and forms new social structures of society.
Under the influence of the rapidly developing system of social communications and information, the information sector of the economy is being formed. A new capital emerges - knowledge. Under the influence of these processes, the nature of labor is changing: unmanned technologies are being introduced, that is, labor itself in direct production disappears, and the participation of workers in production management is expanding.
Information as a tool for promoting progressive ideas contributes to increasing transparency of borders between countries and peoples. Folds up new system public wealth using information technology, where, first of all, human mental abilities are valued.
According to UNESCO, more than half of the total employed population of the most developed countries is directly or indirectly involved in the process of production, storage and dissemination of information. Scientific and technological progress requires government intervention in information exchange and mandatory investment in information spheres activities. Technologies for information exchange must be more effective: thanks to them, people's knowledge and culture will be even more universal. People will become less dependent on the circumstances of place and time that accompany their lives, which should improve the quality and standard of living of society. This means improving the quality of access to information; achieving compliance and quality of services provided to the population, ensuring universal access to information through maximum simplification of interfaces. The development of telecommunications opens up new opportunities in acquiring knowledge and self-realization for people with disabilities and elderly citizens, people working at home, in providing greater opportunities for citizens to perform various roles in society (employees, students, entrepreneurs, etc.); promotes the development of creativity, provides greater opportunities for learning, the development of multilingualism and cultural diversity.
2. The role of information activity in modern society: economic, social, cultural, educational spheres.
The intensive use of information technologies in various spheres of life has significantly changed the understanding of the place and role of information in modern society. When implementing the state scientific and information policy, the main attention should be paid to the creation of a telecommunications infrastructure for information exchange, support of existing information networks and their compatibility with global networks, providing Russian users with access to the global wealth of scientific knowledge.
The use of information technology in science is extremely important. The use of information technologies in science should, on the one hand, develop within the framework of the country's informatization, and on the other, ensure closer interaction between science, education, industry and the social sphere. The introduction of new information technologies will make it possible to organize continuous monitoring of scientific and technical potential, including such aspects as statistics of science and innovation, restructuring of the system of scientific organizations, financing of science, integration of higher education and science, assessment of the results of reforms at both the federal and regional levels .
Modern research in information technology shows that the most effective type of information system that stores heterogeneous information and is an actual means of implementing integration processes is digital libraries(EB). When creating an electronic library, it is necessary to take into account the experience of library and information activities in general, as well as the general organizational principles of the creation, construction and operation of automated library and information systems, including the requirements of international and Russian standards in force in the library field.
Digital libraries are designed to work with heterogeneous information resources, but to ensure user interaction with these resources, a unified language for exchanging information is necessary, which opens up great opportunities for students who participate in this process. After all, electronic information systems are accessible via the Internet, and modern global information networks and the databases included in them provide their users with the broadest opportunities. Therefore, new forms of scientific activity that involve the use of modern information technologies should be fully supported - electronic journals, remote access to databases, teleconferences, etc. This will create new prerequisites for the structural restructuring of scientific organizations and improving the methodology for conducting research and development. In the coming years we will see a process of development mobile computers, mobile television, broadband wireless access, online diaries (“blogs”), RSS technology, and what is called “evolution in progress.”
It turns out that with the use of new information technologies, global opportunities for scientific research and development are opening up.
Assignment for independent work : study the safety instructions and sanitary standards.
Literature:
1. Instructions for labor protection when working on computers - http://*****/instr_pk. htm
2. Rules for safety and behavior in the computer class - http://www. *****/page-1-2-3.html
3. Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the conditions and organization of training in educational institutions - http://www. *****/2011/03/16/sanpin-dok. html
4. Man and the information world - http://*****/filosofiya/chelovek_i_informacionnom_mire. html