Using noindex. How to use an attribute correctly - SEO secrets. Hide links from search robots
We released new book"Content marketing in in social networks: How to get into your subscribers’ heads and make them fall in love with your brand.”

Noindex is an indicator tag for search engines (Yandex and Rambler), warning that part of the web page does not need to be indexed.
More videos on our channel - learn internet marketing with SEMANTICA
![]()
Their first significant difference is that the first was previously visible for Google, and the second was only visible for Yandex and Rambler. Currently, Yandex has also learned to recognize Nofollow, which works only for links, and Nouindex - for any site code.
Using Nofollow does not make the link invisible, but simply indicates that you do not need to follow it and index the document to which it leads. Search robot indexes this hyperlink, but weight is not transferred from the site if it leads to someone else’s resource. This attribute works for all search engines.
As for the Noindex tag, only Yandex works with it. Google will simply ignore it. You need to use it in cases where you want to block some part of the page - text, image or link - from indexing. The search engine recognizes the content, but subsequently removes it from the index. This measure is established for a complete analysis of the page and the procedure for imposing possible sanctions for violations.
What is Noindex for?- Unnecessary/non-unique information is closed, which improves the relevance of the page because the density of key phrases, relevance to the topic, and uniqueness increases.
- End-to-end blocks and hyperlinks are hidden, the presence of which can lead to pessimization.
- Hiding personal and service information, if you don't want it to be easily found through search.
- Closing unnecessary web links.
- Keeping page weight unchanged.
- Distribution of a certain weight across links.
text to hide , and further text.
When working with Noindex, there is a possibility that the validity of the code will decrease, since only the Russian search engine knows this tag. Therefore, the following spelling is recommended:
.
All text that needs to be hidden.
In this case, other search engines will simply miss it, and the validity of the code will remain unchanged.
The Nofollow attribute is applied to linksIn this case, the anchor gets into the index, but the search engine does not follow the web link, the weight on the page remains.
If there is too much Nofollow on a page, this can negatively affect search engine loyalty.
SharingIn order to close both the text part and the hyperlink, you should adhere to the following spelling:
All text that needs to be hidden anchor, and more text
Options correct use Noindex and Nofollow to prevent indexing of the document as a whole
The tag and the attribute go hand in hand all the time, and are often used together. They can be used in the meta name=robots of a document to indicate recommendations for indexing and following web links. An indication to prohibit indexing is necessary if duplicate pages are found, or if confidential or outdated information has appeared on the network, and pages cannot be removed in any other way.
If you want to block the entire page from indexing and prohibit the registration of links located on it, you must indicate the following in the page metadata:
Nowindex creates a command for Yandex not to index the content on the page, but the robot follows its web links. Therefore, additional Nofollow indicates not to walk on them. This instruction is accepted by both Yandex and Google.
Regarding deleting a document from Google index, then the search engine provides alternative method: entry X-Robots-Tag: noindex, nofollow. This indication is fixed in http headers, which are not visible in the page code.
We talk about the difference between Nofollow and Noindex, how to use them correctly for links and hiding content on the site.
Always make sure that the tags and attributes discussed in the article are present in the right places to get exactly the result you expect.
Good day, dear readers. I often come across the fact that many novice webmasters and bloggers are completely confused about the use of noindex and nofollow. Let's figure out what it is, what it's eaten with, and dot the i's.
It’s worth starting with so that in the future you never have confusion in your head that both noindex and nofollow are used in two relatively different meanings in a web document.
The first is inside the ROBOTS meta tag (not to be confused with the robots.txt file) in the value of the content attribute. This meta tag relates to the entire document as a whole. Second, only nofollow is used - inside the tag and relates to a specific link. The noindex tag is a slightly different story, and we will also talk about it today. It is also worth noting that I will only consider the use of nofollow and noindex in two search engines - Yandex and Google.
NOINDEX and NOFOLLOW in the ROBOTS meta tagThe robots meta tag is responsible for the entire page. Using this meta tag, you can prohibit or allow indexing of page content.
Noindex is responsible for prohibiting indexing of text on the page.
Nofollow is responsible for preventing the indexing of links on a page.
These values are used as follows:
which means that this page cannot be indexed at all.
There may also be the following values:
you can index the content, but ignore the links on the page, i.e. don't index them.
You can read more about the robots meta tag in my article.
NOFOLLOW in linksNofollow is used as the value of the rel attribute in the tag . And is responsible for indexing each specific link on the page.
The rel attribute shows the relationship of this document to the document being referenced.
In this case, by setting the rel attribute to nofollow, we are asking the search engine not to follow the external link, and we are also emphasizing that we are not responsible for the content that we link to.
Links designed with this value do not convey the authority of our page, in other words, the TCI and Page Rank are not transmitted. However, it is also worth considering that in the case of PR, the weight still goes, but not to the site to which we link, but to nowhere in the literal sense of the word. Regarding the TCI, there is no exact information about whether the weight is lost or remains on the site.
Let's take a closer look at the distribution and transfer of weight to Google.
So, it doesn’t matter at all how many links you have have the attribute and how many do not. If there are 10 links on a page, then each link will receive part of the authority of your page, and each of them will transfer this weight, but if in one case the weight is transferred to a specific site, then in another case the weight will simply go to nowhere.

Let's imagine a little how a search engine sees the World Wide Web. All sites are interconnected by links, absolutely everything. The first refers to the second, the second to the third... the thousandth to the thousand and one and some million in the end will definitely refer to the first.
Thus the chain is closed, all sites are in a loop, and the weight that the first site transfers always returns to it through hundreds and thousands of other sites. We also don’t forget, and I already wrote about this in, that this weight is transferred not just once, but constantly, and over time the weight only becomes larger, increasingly increasing its authority. It is on this principle that website linking is built.
Now imagine that the first site closed its links with the . The weight will not transfer to the second site, but will flow into nowhere, and the second site will not receive that part of the weight that it should have, will not be able to transfer it further along the chain, and as a result, having gone through the entire cycle, X is some site that should was to transfer the weight to the first site, it will transfer it in significantly less quantity than it could. So, each time you don’t receive that part of the weight that you yourself throw into nowhere by closing your links with the attribute, the site cannot transfer it to you, which means that by closing your links, you deprive yourself of increasing weight, and such an indicator as PR
To make this easier to understand, let's imagine that each link conveys a weight equal to one.

Thus, if the first site did not close the link with the attribute, then at the end of the cycle it will receive more weight from incoming links than if outgoing links are closed.
Closing a link is not profitable if you really, truly recommend to your readers the article you are linking to, your page on a social network, or your RSS feed. It’s stupid to close links to your own pages on social networks when you recommend that your readers subscribe to blog updates through them. After all, these are your own pages, your own RSS feed, which broadcasts your own content. Aren't you responsible for it yourself?
But there are situations when it is really necessary to close links with the nofollow value. Let's turn to the sources, Yandex and Google, what do they say about this?


In addition to this, Google recommends marking selling links with the attribute. Google also writes that using nofollow we can point the robot to closed sections of our site, but clarifies that there are other ways to indicate this.
I would also like to pay attention to one more point. Some ardent fighters for closed links focus not only on the links themselves, i.e. in the tag , but also wherever your imagination allows. And in the tag, and, and in the tag .
Let's not invent our own standards, but turn to the existing ones that are being developed by the international organization W3C.
The value can only be used in a tag , and it cannot be used in other tags!
So, we found out when it is worth using the link attribute and when it is not advisable. We will also no longer be inserting it anywhere except in one single tag indicating the link. Now let's pay attention to the noindex tag.
NOINDEX - a rudiment from YandexOnce upon a time, Yandex did not understand the meaning of nofollow, and therefore came up with its own tag
something inside
so that you can close unwanted links with its help. Everything that was inside this tag was ignored by the Yandex robot. But a lot of water has passed under the bridge since then, Yandex has matured and began to understand the . This happened back in the spring of 2010. That's when the noindex tag lost its value as a link-closing tool. But at the same time, another meaning remains - to hide text content. Excerpt from the Yandex Help section:

They are recommended to hide service areas of the text. It is not entirely clear what service areas we are talking about, but it is quite obvious that this tag now has nothing to do with links. Those. it turns out if we place the link in this tag:
You can safely refuse to use this tag, especially considering its invalidity. After all, in fact, such a tag does not exist at all. As we know, HTML standards are developed by the international organization W3C, and there is no such tag in the specification for the HTML language; this is completely an invention of Yandex.
There is one more question that I would like to draw your attention to. Often, when I try to explain what I wrote about in this article, people object to me:
“I analyze the site with such and such a tool, and it shows me that my links are not closed...
You can trust all these tools, this is your full right, but isn’t it better to believe the official documentation of search engines, and isn’t it better to think with your own head?
Good luck with website optimization.
Hello, dear visitors!
If you came to this page, then most likely, somewhere you were advised to use the noindex tag to block any content from indexing.
In this article I will briefly tell you why it is needed and the features of its use. I’ll also show you where I use it on my website.
General informationAs with the attribute, which I recommend familiarizing yourself with, noindex has meanings for both a regular tag and a meta tag.
- The noindex tag only blocks those parts that are contained within it from indexing;
- Meta tag noindex - blocks the entire page from indexing.
In the first case, the tag wraps the necessary parts of the text on pages that do not need to be indexed. These could be official sections of text or some kind of confidential information.
The tag can be used, both in the generally accepted version and in the valid one, to make the page code valid and remove errors due to the tag. Below I give 2 lines, the first of which is a normal option, and the second is a valid one.
here is a piece of content that needs to be closed
Which option to use, decide for yourself. I came to the second one.
In the case of a meta tag, noindex is added to the site header, which prevents the entire page from being indexed. Necessary in the same case (service pages and so on), only for a full page.
In this case, noindex is the value of the robots meta tag (see below).
Now regarding the use of this tag.
ApplicationAs I already wrote above, it is worth using it if there is some kind of service information on the page. This also occurs when there are non-unique pieces of text that have a detrimental effect on the page's progress. They can also be closed with the noindex tag.
If we take a meta tag that applies to the entire page and is contained inside the robots meta tag (screenshot above), then this case should be used to block entire pages from indexing. These can be entire service pages that do not provide any benefit to the site and visitors. For example, contact pages, site maps, and so on.
There is also a closure of pagination pages, that is, those pages that are divided into lists. For example, in page navigation on a site, you can close all pages except the first one to protect yourself from duplicate content.

Although, recently I stopped closing pages with the noindex meta tag. This is due to my analysis of other popular sites. I saw that none of the giants use such a closure. Based on this, I also removed it. Although before I added noindex to such pages and everything worked with a bang. Therefore, if you add a meta tag to pagination pages, then you don’t have to worry.
The main thing is that the content pages themselves are completely open and do not have the noindex meta tag.
You can check its availability at source code pages by pressing the key combination ctrl+u.
Regarding my site, I use the tag quite often, but not in the articles themselves, but in the template layout itself. I close all parts that do not provide meaning to the site:
- social buttons;
- subscription forms;
- on the pages of categories, archives and search, I close the text of the short announcement so as not to duplicate the content, because it is also available in full version articles.
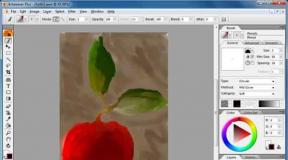
You can check the closed parts of this tag using the RDS bar browser add-on.
Here's what closing the subscription form and social buttons looks like when the RDS bar is active (closed areas are highlighted in brown).

And here is a closed piece of text on the pages of categories, archives and search.

This way you can close a lot of unnecessary things in your template.
This concludes this material. Nothing more can be said about this tag. In conclusion, I want to say that if you want to close external links in noindex, then only the content of the link, that is, its anchor, will be closed.
If you still have any questions about the noindex tag, write them in the comments under the block of similar posts, which you can also read. I assure you, it will be interesting.
All friends. See you later.
Best regards, Konstantin Khmelev!
Hello, dear readers of the blog site. Today I want to touch on the problem of understanding whether it is now possible to use noindex in order to block a link from indexing search engines Yandex and Google, because over the past six months or a year there has been a fundamental change in the nofollow algorithm.
The problem here is that Google has changed the principle of calculating static weight when using rel nofollow, and this change has long been hotly discussed in various thematic forums on website promotion and optimization.
What is the impact of rel nofollow and the noindex tag?And Yandex also did not lag behind its biggest competitor in the Runet search market and, starting in 2010, changed its attitude towards nofollow (it began to take it into account).

Previously, the RuNet mirror ignored it, but now, as can be seen from the screenshot of the help taken on this page, this attribute works and is taken into account.
The noindex tag, which Yandex single-handedly introduced into circulation and which until some time was the only alternative to nofollow, now does not in any way affect the accounting of the link it closed.
But using it you can still block individual fragments of a web page from indexing. This tag is paired and everything that falls between its opening and closing elements will not be taken into account by the search.

Because but the index was purely our local invention, it is natural that it was not included in the register of allowed tags current version HTML language 4.01 and the validator still complains about it.
To avoid this, you can use it as a , as shown in the screenshot above. In this case, naturally, there will be no swearing, because you can write whatever you want in the comments.
text to be prevented from being indexed
Yandex writes on its help page that noindex and nofollow should be interpreted in exactly the same way as similar values that are used in .

Those. nofollow prohibits the search robot from following this link, and noindex prohibits adding the text fragment contained in it to the index.
Google has never taken noindex into account at all and, naturally, successfully ignores it, just like any other search engine except Yandex. The attitude towards calculating static weight on pages where . Previously, they could not be taken into account at all, but now everything has become a little more complicated and sadder.
But telling everything in a nutshell is not our method. Therefore, I will now let the “water out” a little, as some gentlemen put it in the comments, and will try to show the current situation using fingers and abstract examples. Yes, I’ll immediately make a reservation that my opinion is in no way the absolute truth, for it only expresses my point of view on this problem. Thanks in advance to all commentators, because truth is born in dispute.
So, let's first go back a little and see how it was possible to block hyperlinks for search engines from indexing using the nofollow and noindex tags (most often they still try to block external backlinks from indexing, because they contribute to the leakage of static weight, but let's talk about that a little bit later).
So, link texts, which are also called anchors, allow Yandex and Google to carry out so-called link ranking, which significantly affects the position of the resource in search results. It is for this reason that in order to promote a site for any request (to help you), optimizers try to purchase as many backlinks as possible with texts (anchors) containing from the request for which this page is being promoted.
At one time, a number of enthusiasts made it so that the request “pathetic loser” opened the resource of the then President of America Bush Jr. What is noteworthy is that these keywords were not found on the resource itself, but a giant reference mass with this text (anchor), which resulted in such an incident.
Now such a trick will not work, because link ranking does not have such a colossal influence on ranking and it is necessary that this phrase be found on the Bush portal itself, which is unlikely.
But the role of links in search engine promotion does not end there, because search algorithms necessarily calculate the so-called static weight for each page of each individual resource. It's possible that different systems they calculate it slightly differently, but the essence remains unchanged - the status weight is transferred to the page only via a hyperlink and its anchor is not taken into account.
True, any page (document, as search engines call them) immediately after its appearance (indexing) has an initial minimum static weight (), which can be increased unlimitedly due to incoming external and internal links to this page. The key point here is that it is transmitted not only by external, but also by internal links.
Moreover, the document, referring to other external or internal pages, does not at all lose its static weight (pr for Google or for Yandex), which entirely depends only on the number and weight of hyperlinks included in it. By the latter, I mean the own status of donor pages (donors are those from where backlinks are placed on your document, which in this case acts as an acceptor).
How to block external links from indexingRemember when puzzles about a swimming pool with several incoming and outgoing pipes were once popular in school? There it was still necessary to calculate either the time to fill the pool or the water level in it. But that's not the point. I just want to take as an abstract example for greater clarity just such a pool, and not a simple one, but with a number of assumptions.
Each document on the site can be presented as a separate pool, into which water will be supplied through a series of pipes of different diameters (our incoming internal and external hyperlinks from documents with different static weights), and there will also be a series of pipes through which water will flow to other documents yours or any other resource (outgoing internal and external links).
The water level in the pool will be equivalent to the static weight gained by this document (the web page of your resource). The assumption will be that water flowing through the pipes of outgoing links will not reduce the water level in the pool (static weight of the document).
Now look carefully. Let’s say that we have 4 internal links and one external link from one document (in the analogy with a swimming pool, this will be equivalent to five outgoing pipes of the same cross-section). As a result, the maximum status weight that this document (web page) can convey will be divided into exactly 5 parts and only one-fifth of this weight will be transferred to each of the 4 internal documents, and one-fifth will go to the external one.
Now imagine that you have the opportunity to ask the search engines Yandex and Google not to index this very one external link (close it or, in the analogy with a swimming pool, turn off the valve on the pipe that does not lead to your project).
Then the maximum weight of the document that it can transmit will no longer need to be divided into 5 parts, but only into 4, which will allow the internal links of the document to receive one quarter, and not one fifth, of the maximum weight that this web page is capable of giving.
It seems like a trifle, but if your resource has a thousand pages, and you block several end-to-end external links from indexing (which will be present in all documents, for example, with), then the total increase in status will be noticeable. But it directly affects the position of your resource in Yandex and Google rankings (of course, all other optimization conditions being equal).
I think that we have dealt with the question of why to block external hyperlinks from indexing, and now all that remains is to figure out how to do this? Previously, everything was simple - enclose a hyperlink you don’t need in the opening and closing noindex tag so that Yandex does not take it into account, and HTML tag links A, you specify an attribute (for Google), for example, like this:
External resource
In WordPress, to automate the process of blocking all external links from indexing, you can use, for example, . When using it, if you add a special class to the hyperlink tag, it will remain open for indexing by search engines. This may be necessary, for example, when placing a link in a post or advertising review.
The static weight was not transmitted through the hyperlink closed in this way and the internal pages of your site, as a result, received a slightly higher value than in the case of an open one external link. But it was like that before, but now everything has become very, very problematic.
This only applies to maintaining status on the site. Here it is important to understand that, for example, in comments it is simply necessary to close links from indexing, because a large number of links to spam resources (are you able to check all the resources of commentators?) will make your project also spam in the eyes of search engines.
So, let's return to the fact that Google has changed the algorithm of work - now the link in which this attribute is inserted will not transfer static weight to the document, but at the same time this will not increase the share of weight transferred to internal pages, according to the specified with of this document internal hyperlinks.
If we return to our example with a pool and pipes, then the situation with, which was before the innovation, can be represented as closing the valve on the pipe leading to another resource. And at the same time, more water (static weight) flowed through the remaining pipes (internal).
But the current situation looks like tearing out an external pipe by the roots - the link weight will no longer flow to the external resource, but we will also have a hole in the pool, and therefore, the internal pages of your resource will continue to receive less static weight.
How Yandex takes into account rel nofollow and noindexWe all spoke for Google, but what is the situation with the use of Yandex, because this is our unforgettable search leader in RuNet. Here everything is much more vague, because there are no clear opinions on this issue.
But it seems that the RuNet mirror, after it began to take into account rel nofollow in hyperlink tags, removed from noindex any influence on the ban on indexing links.
Now noindex serves one single purpose - to block some text fragments from indexing in Yandex and Rambler. And if you use it for links, then it will simply prohibit these search engines from indexing the text (anchor), but the hyperlink itself and the status weight transmitted through it will still be taken into account and taken into account.
Another question is how does Yandex take rel nofollow into account? Is it copying the work scheme of the old Google or did it immediately adopt a redesigned calculation algorithm? Personally, I find it difficult to answer this question, but I believe that we should count on the worst case scenario.
Then it turns out that you and I no longer have the tools that allow us to fully block links from indexing, so that there is no leakage of weight from the site into the void.
As before, we can block entire pages or hyperlinks to them from indexing using the Robots meta tag, the purpose of which is described in the article given at the beginning of the publication, but difficulties arise with individual links and rel nofollow is no longer a good solution for this problem.
You can, of course, add external hyperlinks through redirects or Java, but Google has already learned to take them into account, and Yandex, if it hasn’t learned yet, will definitely learn soon. In this regard, it is not at all clear what to do with backlinks from comments and visit counters. In any case, they will suck static weight from the site into the void (if they are closed in nofollow), or to the resources of commentators or counters (in case they refuse to use it).
Some webmasters, by the way, use external nofollow in comments, although this does not mean closing external hyperlinks at all, but means opening the page in an external window (analogous to the target="_blank" attribute, which in XHTML has become invalid, i.e. does not correspond standards), but this external will only work in conjunction with a specially written script in javascript. In general, this is a completely different topic and has nothing to do with closing from indexing.
Actually, I decided to try to remove backlinks from comments altogether and see how it affects general position my blog both in Google and Yandex. If there are no changes for the better, then I will return everything as it was. The experiment will probably turn out to be representative, because I have about 6,000 comments and most of them have a backlink to the commentator’s resource.
If anyone is interested, then remove the links from WordPress comments quite simple. You will need help ftp client(manager) FileZilla connect via FTP and open the comments.php file for editing from the folder with the WordPress theme you are using. In it you need to find the place where the following piece of code is written:
and replace it with a slightly modified version:
And also, in order to remove the line for entering the URL from the form for adding a new comment, you will need to remove a similar section of code: